Numeration systems are the backbone of our numerical communication, shaping how we perceive and interact with numbers. In this article, we’ll dive into two major numeration systems: the Indian System and the International System. By understanding these systems, we gain insight into the fascinating world of numbers and their representations.
Indian System of Numeration: Unraveling the Complexity
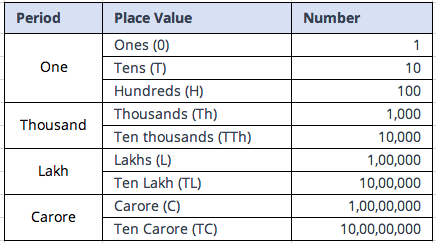
The Indian System of Numeration, also known as the Eastern Arabic Numerals, has deep historical roots and a unique structure. Let’s explore its intricacies through a breakdown:
Decimal Point and Thousands Separator: National systems vary significantly in their usage of the decimal point and thousands separator. For instance, while some countries opt for commas and periods, others employ spaces and apostrophes.
Large Number Naming: Cultural influences permeate large number names, resulting in unique terms like “Lakh” and “Crore” in the Indian system. These terms carry linguistic and historical significance.
Contextual Understanding: National systems provide localised insights, reflecting a country’s cultural context. However, this can pose challenges in international contexts due to diverse interpretations.
International System of Numeration: Bridging Global Communication
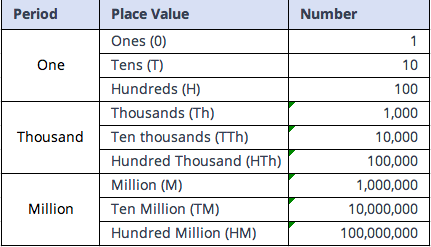
The International System of Numeration, also called the Western Arabic Numerals, is a universal language for numbers, extensively used in various fields. Let’s break down its structure:
Decimal Point and Thousands Separator: The international system prioritizes consistency with a period as the decimal point and a space as the thousands separator. This uniformity aids cross-border clarity.
Simplified Number Naming: For larger numbers, the international system uses straightforward terms like “Million” and “Billion,” making them universally comprehensible and eliminating language barriers.
Global Communication: By establishing a standardised framework, the international system facilitates effective cross-cultural communication in scientific, financial, and technical spheres.
Comparing the Approaches: Tradition Meets Standardization
Cultural Heritage vs. Global Consistency: National systems celebrate cultural heritage, while the international system prioritizes universal understanding through standardized conventions.
Nuanced Representation vs. Clear Communication: National systems offer nuanced representation within their cultural milieu. Conversely, the international system ensures clear and unambiguous communication across borders.
Contextual Flexibility vs. Precision: National systems allow for context-specific adaptations, but the international system’s precision is pivotal in fields demanding exact numerical representation.
Conclusion: Embracing Harmony in Diversity
Numeration systems, whether national or international, mirror humanity’s ingenious adaptability. As the world intertwines, embracing both approaches enhances our ability to communicate effectively across diverse contexts. While national systems honor cultural legacies, the international system empowers us to overcome language barriers and collaborate seamlessly on a global scale.
In our shared numerical journey, these systems stand as testaments to the beauty of diversity and the power of standardisation, bridging cultures and connecting minds through the universal language of numbers.
